Oracle Data Miner
Oracle Analytics Sessions at COLLABORATE12
There are a number of Oracle Advanced Analytics and related topics taking place this week at COLLABORATE12 in Las Vegas (http://collaborate12.com).
| Date | Time | Presentation | Presenter |
| Sun 22nd | 9:00-3pm | Oracle Business Intelligence Application Journey | |
| Mon 23rd | 9:45-10:45 | Managing Unstructured Data using Hadoop, Oracle 11g and Oracle Exadata Database Machine | Jim Steiner |
| Mon 23rd | 9:45-10:45 | Environmental Data Management and Analytics-a Real World Perspective | Angela Miller |
| Mon 23rd | 11-12 | Public Safety and Environmental Real-Time Analytics using Oracle Business Intelligence | Raghav Venkat Therese Arguelles |
| Mon 23rd | 11-12 | BI is more than slice and dice | Peter Scott |
| Mon 23rd | 14:30-15:30 | In-Database Analytics: Predictive Analytics, Data Mining, Exadata & Business Intelligence | Jacek Myczkowski |
| Mon 23rd | 15:45-16:45 | Big Data Analytics, R you ready | Mark Hornick Shyam Nath |
| Tues 24th | 10:45-11:45 | BI Analytics and Oracle NoSQL. The Future of Now | Manish Khera |
| Wed. 25th | 8:15-9:15 | Oracle Data Mining – A Component of the Oracle Advanced Analytics Option-Hands-on Lab | Charlie Berger |
| Wed 25th | 9:30-10:30 | Oracle R Enterprise – A Component of the Oracle Advanced Analytics Option-Hands-on Lab | Mark Hornick |
Here are the abstracts from the two main Oracle Advanced Analytics presentations by Charlie Berger and Mark Hornick
Oracle Data Mining – A Component of the Oracle Advanced Analytics Option
This Hands-on Lab provides an introduction to Oracle Data Mining and the Oracle Data Miner GUI.
Oracle Data Mining (ODM), now part of Oracle Advanced Analytics, provides an extensive set of in-database data mining algorithms that solve a wide range of business problems. It can predict customer behavior, detect fraud, analyze market baskets, segment customers, and mine text to extract sentiments. ODM provides powerful data mining algorithms that run as native SQL functions for in-database model building and model deployment. There is no need for the time delays and security risks of data movement.
The free Oracle Data Miner GUI is an extension to Oracle SQL Developer 3.1 that enables data analysts to work directly with data inside the database, explore the data graphically, build and evaluate multiple data mining models, apply ODM models to new data, and deploy ODM’s predictions and insights throughout the enterprise. Oracle Data Miner work flows capture and document the user’s analytical methodology and can be saved and shared with others to automate advanced analytical methodologies.
Oracle R – A component of the Oracle Advanced Analytics Option
This Hands-on Lab provides an introduction to Oracle R Enterprise.
Oracle R Enterprise, a part of the Oracle Advanced Analytics Option, makes the open source R statistical programming language and environment ready for the enterprise by integrating R with Oracle Database. R users can interactively and transparently execute R scripts for statistical and graphical analyses on data stored in Oracle Database. R scripts can be executed in Oracle Database using potentially multiple database-managed R engines – resulting in data parallel execution. ORE also provides a rich set of statistical functions and advanced analytics techniques.
In this lab, attendees will be introduced to Oracle’s strategy for R, including the Oracle R Distribution, Oracle R Enterprise (ORE), and Oracle R Connector for Hadoop (ORCH). We will focus on Oracle R Enterprise with hands-on exercises exploring the transparency layer, embedded R execution, and statistics engine.
Data Visualization Videos & Resources
Here is a selection of videos and websites on Data Visualisations.
Hans Rosling videos of his TED talks
- World Population Growth
- Global Population Growth (TED)
- Asia’s Rise – How and When
- HIV: New facts and stunning data visuals
- Video for the BBC
Other videos
Useful Websites
Oracle Advanced Analytics Video by Charlie Berger
Charlie Berger (Sr. Director Product Management, Data Mining & Advanced Analytics) as produced a video based on a recent presentation called ‘Oracle Advanced Analytics: Oracle R Enterprise & Oracle Data Mining’.
This is a 1 hour video, including some demos, of product background, product features, recent developments and new additions, examples of how Oracle is including Oracle Data Mining into their fusion applications, etc.
Oracle has 2 data mining products, with main in-database Oracle Data Mining and the more recent extensions to R to give us Oracle R Enterprise.
Check out the video – Click here.
Check out Charlie’s blog at https://blogs.oracle.com/datamining/
Oracle University : 2 Day Oracle Data Mining training course
2 Day Oracle Data Miner training course by Oracle University
In the past few days Oracle University has advertised a new 2 Day instructor led training course on Oracle Data Miner.
There are no advertised dates or locations for this course yet. I suppose it will depend on the level of interest in the product.
There is the overview from the Oracle University webpage
“In this course, students review the basic concepts of data mining and learn how leverage the predictive analytical power of the Oracle Database Data Mining option by using Oracle Data Miner 11g Release 2. The Oracle Data Miner GUI is an extension to Oracle SQL Developer 3.0 that enables data analysts to work directly with data inside the database.
The Data Miner GUI provides intuitive tools that help you to explore the data graphically, build and evaluate multiple data mining models, apply Oracle Data Mining models to new data, and deploy Oracle Data Mining’s predictions and insights throughout the enterprise. Oracle Data Miner’s SQL APIs automatically mine Oracle data and deploy results in real-time. Because the data, models, and results remain in the Oracle Database, data movement is eliminated, security is maximized and information latency is minimized”
Click on the following link to access the details of the training course
http://education.oracle.com/pls/web_prod-plq-dad/db_pages.getCourseDesc?dc=D73528GC10
To view a PDF of the course details – click here
ODM–Attribute Importance using PL/SQL API
In a previous blog post I explained what attribute importance is and how it can be used in the Oracle Data Miner tool (click here to see blog post).
In this post I want to show you how to perform the same task using the ODM PL/SQL API.
The ODM tool makes extensive use of the Automatic Data Preparation (ADP) function. ADP performs some data transformations such as binning, normalization and outlier treatment of the data based on the requirements of each of the data mining algorithms. In addition to these transformations we can specify our own transformations. We do this by creating a setting tables which will contain the settings and transformations we can the data mining algorithm to perform on the data.
ADP is automatically turned on when using the ODM tool in SQL Developer. This is not the case when using the ODM PL/SQL API. So before we can run the Attribute Importance function we need to turn on ADP.
Step 1 – Create the setting table
CREATE TABLE Att_Import_Mode_Settings (
setting_name VARCHAR2(30),
setting_value VARCHAR2(30));
Step 2 – Turn on Automatic Data Preparation
BEGIN
INSERT INTO Att_Import_Mode_Settings (setting_name, setting_value)
VALUES (dbms_data_mining.prep_auto,dbms_data_mining.prep_auto_on);
COMMIT;
END;
Step 3 – Run Attribute Importance
BEGIN
DBMS_DATA_MINING.CREATE_MODEL(
model_name => ‘Attribute_Importance_Test’,
mining_function => DBMS_DATA_MINING.ATTRIBUTE_IMPORTANCE,
data_table_name > ‘mining_data_build_v’,
case_id_column_name => ‘cust_id’,
target_column_name => ‘affinity_card’,
settings_table_name => ‘Att_Import_Mode_Settings’);
END;
Step 4 – Select Attribute Importance results
SELECT *
FROM TABLE(DBMS_DATA_MINING.GET_MODEL_DETAILS_AI(‘Attribute_Importance_Test’))
ORDER BY RANK;
ATTRIBUTE_NAME IMPORTANCE_VALUE RANK
——————– —————- ———-
HOUSEHOLD_SIZE .158945397 1
CUST_MARITAL_STATUS .158165841 2
YRS_RESIDENCE .094052102 3
EDUCATION .086260794 4
AGE .084903512 5
OCCUPATION .075209339 6
Y_BOX_GAMES .063039952 7
HOME_THEATER_PACKAGE .056458722 8
CUST_GENDER .035264741 9
BOOKKEEPING_APPLICAT .019204751 10
ION
CUST_INCOME_LEVEL 0 11
BULK_PACK_DISKETTES 0 11
OS_DOC_SET_KANJI 0 11
PRINTER_SUPPLIES 0 11
COUNTRY_NAME 0 11
FLAT_PANEL_MONITOR 0 11
What has Oracle done to R to give us ORE
Oracle R Enterprise (ORE) was officially launched over the past couple of days and it has been receiving a lot of interest in the press.
We now have the Oracle Advanced Analytics (OAA) option which comprises, the already existing, Oracle Data Mining and now Oracle R Enterprise. In addition to the Oracle Advanced Analytics option we also 2 free set of tools available to use to use. The first of these free tools are the statistical functions which are available in all versions of the Oracle Database and the second free tool is the Oracle Data Miner tool that is part of the newly released SQL Developer 3.1 (7th Feb).
What has Oracle done to Oracle to make Oracle R Enterprise ?
The one of the main challenges with using R is that it is memory constrained, resulting in the amount of data that it can process. So the ORE development team have worked ensuring R can work transparently with data within the database. This removes the need extract the data from the database before it can be used by R. We still get all the advanced on in-Database Data Mining.
They have also embedded R functions within the database, so we an run R code on data within the database. By having these functions with the database, this allows R to use the database parallelism and so we get quicker execution of our code. Most R implementation are constrained to being able to process dataset containing 100Ks of records. With ORE we can now process 10M+ records
In addition to the ORE functions and algorithms that are embedded in the database we can also use the R code to call the suite of data mining algorithms that already exist as part of Oracle Data Miner.
For more details of what Oracle R Enterprise is all about check out the following links.
ODM 11gR2–Attribute Importance
I had a previous blog post on Data Exploration using Oracle Data Miner 11gR2. This blog post builds on the steps illustrated in that blog post.
After we have explored the data we can identity some attributes/features that have just one value or mainly one value, etc. In most of these cases we know that these attributes will not contribute to the model build process.
In our example data set we have a small number of attributes. So it is easy to work through the data and get a good understanding of some of the underlying information that exists in the data. Some of these were pointed out in my previous blog post.
The reality is that our data sets can have a large number of attributes/features. So it will be very difficult or nearly impossible to work through all of these to get a good understanding of what is a good attribute to use, and keep in our data set, or what attribute does not contribute and should be removed from the data set.
Plus as our data evolves over time, the importance of the attributes will evolve with some becoming less important and some becoming more important.
The Attribute Importance node in Oracle Data Miner allows use to automate this work for us and can save us many hours or even days, in our work on this task.
The Attribute Importance node using the Minimum Description Length algorithm.
The following steps, builds on our work in my previous post, and shows how we can perform Attribute Importance on our data.
1. In the Component Palette, select Filter Columns from the Transforms list
2. Click on the workflow beside the data node.
3. Link the Data Node to the Filter Columns node. Righ-click on the data node, select Connect, move the mouse to the Filter Columns node and click. the link will be created
4. Now we can configure the Attribute Importance settings.Click on the Filter Columns node. In the Property Inspector, click on the Filters tab.
– Click on the Attribute Importance Checkbox
– Set the Target Attribute from the drop down list. In our data set this is Affinity Card
5. Right click the Filter Columns node and select Run from the menu
After everything has run, we get the little green box with the tick mark on the Filter Column node. To view the results we right clicking on the Filter Columns node and select View Data from the menu. We get the list of attributes listed in order of importance and their Importance measure.
We see that there are a number of attributes that have a zero value. It algorithm has worked out that these attributes would not be used in the model build step. If we look back to the previous blog post, some of the attributes we identified in it have also been listed here with a zero value.
ODM 11gR2–Real-time scoring of data
In my previous posts I gave sample code of how you can use your ODM model to score new data.
Applying an ODM Model to new data in Oracle – Part 2
Applying an ODM Model to new data in Oracle – Part 1
The examples given in this previous post were based on the new data being in a table.
In some scenarios you may not have the data you want to score in table. For example you want to score data as it is being recorded and before it gets committed to the database.
The format of the command to use is
prediction(ODM_MODEL_NAME USING )
prediction_probability(ODM_Model_Name, Target Value, USING )
So we can list the model attributes we want to use instead of using the USING * as we did in the previous blog posts
Using the same sample data that I used in my previous posts the command would be:
Select prediction(clas_decision_tree
USING
20 as age,
‘NeverM’ as cust_marital_status,
‘HS-grad’ as education,
1 as household_size,
2 as yrs_residence,
1 as y_box_games) as scored_value
from dual;
SCORED_VALUE
————
0
Select prediction_probability(clas_decision_tree, 0
USING
20 as age,
‘NeverM’ as cust_marital_status,
‘HS-grad’ as education,
1 as household_size,
2 as yrs_residence,
1 as y_box_games) as probability_value
from dual;
PROBABILITY_VALUE
—————–
1
So we get the same result as we got in our previous examples.
Depending of what data we have gathered we may or may not have all the values for each of the attributes used in the model. In this case we can submit a subset of the values to the function and still get a result.
Select prediction(clas_decision_tree
USING
20 as age,
‘NeverM’ as cust_marital_status,
‘HS-grad’ as education) as scored_value2
from dual;
SCORED_VALUE2
————-
0
Select prediction_probability(clas_decision_tree, 0
USING
20 as age,
‘NeverM’ as cust_marital_status,
‘HS-grad’ as education) as probability_value2
from dual;
PROBABILITY_VALUE2
——————
1
Again we get the same results.
ODM 11gR2–Using different data sources for Build and Testing a Model
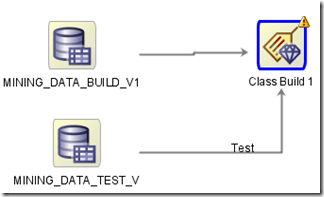
There are 2 ways to connect a data source to the Model build node in Oracle Data Miner.
The typical method is to use a single data source that contains the data for the build and testing stages of the Model Build node. Using this method you can specify what percentage of the data, in the data source, to use for the Build step and the remaining records will be used for testing the model. The default is a 50:50 split but you can change this to what ever percentage that you think is appropriate (e.g. 60:40). The records will be split randomly into the Built and Test data sets.
The second way to specify the data sources is to use a separate data source for the Build and a separate data source for the Testing of the model.
To do this you add a new data source (containing the test data set) to the Model Build node. ODM will assign a label (Test) to the connector for the second data source.
If the label was assigned incorrectly you can swap what data sources. To do this right click on the Model Build node and select Swap Data Sources from the menu.
Updating your ODM (11g R2) model in production
In my previous blog posts on creating an ODM model, I gave the details of how you can do this using the ODM PL/SQL API.
But at some point you will have a fairly stable environment. What this means is that you will know what type of algorithm and its corresponding settings work best for for your data.
At this point you should be able to re-create your ODM model in the production database. The frequency of doing this update is dependent on number of new cases that you have. So you need to update your ODM model could be daily, weekly, monthly, etc.
To update your model you will need to:
– Creating a settings table for your model
– Create a new ODM model
– Rename your new ODM model to the production name
The following examples are based on the example data, model names, etc that I’ve used in my previous post.
Creating a Settings Table
The first step is to create a setting table for your algorithm. This will contain all the parameter settings needed to create the new model. You will have worked out these setting from your previous attempts at creating your models and you will know what parameters and their values work best.
— Create the settings table
CREATE TABLE decision_tree_model_settings (
setting_name VARCHAR2(30),
setting_value VARCHAR2(30));
— Populate the settings table
— Specify DT. By default, Naive Bayes is used for classification.
— Specify ADP. By default, ADP is not used.
BEGIN
INSERT INTO decision_tree_model_settings (setting_name, setting_value)
VALUES (dbms_data_mining.algo_name,
dbms_data_mining.algo_decision_tree);
INSERT INTO decision_tree_model_settings (setting_name, setting_value)
VALUES (dbms_data_mining.prep_auto,dbms_data_mining.prep_auto_on);
COMMIT;
END;
Create a new ODM Model
We will need to use the DBMS_DATA_MINING.CREATE_MODEL procedure. In our example we will want to create a Decision Tree based on our sample data, which contains the previously generated cases and the new cases since the last model rebuild.
BEGIN
DBMS_DATA_MINING.CREATE_MODEL(
model_name => ‘Decision_Tree_Method2′,
mining_function => dbms_data_mining.classification,
data_table_name => ‘mining_data_build_v’,
case_id_column_name => ‘cust_id’,
target_column_name => ‘affinity_card’,
settings_table_name => ‘decision_tree_model_settings’);
END;
Rename your ODM model to production name
The model we have create created above is not the name that is used in our production software. So we will need to rename it to our production name.
But we need to be careful about when we do this. If you drop a model or rename a model when it is being used then you can end up with indeterminate results.
What I suggest you do, is to pick a time of the day when your production software is not doing any data mining. You should drop the existing mode (or rename it) and the to rename the new model to the production model name.
DBMS_DATA_MINING.DROP_MODEL(‘CLAS_DECISION_TREE‘);
and then
DBMS_DATA_MINING.RENAME_MODEL(‘Decision_Tree_Method2’, ‘CLAS_DECISION_TREE’);
Oracle Analytics Update & Plan for 2012
On Friday 16th December, Charlie Berger (Sr. Director, Product Management, Data Mining & Advanced Analytics) posted the following on the Oracle Data Mining forum on OTN.
“… soon you’ll be able to use the new Oracle R Enterprise (ORE) functionality. ORE is currently in beta and is targeted to go General Availability in the near future. ORE brings additional functionality to the ODM Option, which will then be renamed to the Oracle Advanced Analytics Option to reflect the significant adv. analytical functionality enhancements. ORE will allow R users to write R scripts and run them inside the database and eliminate and/or minimize data movement in/out of the DB. ORE will provide R to SQL transparency for SQL push-down to in-DB SQL and and expanding library of Oracle in-DB statistical functions. Packages that cannot be pushed down will be run in embedded R mode while the DB manages all data flows to the multiple R engines running inside the DB.
In January, we’ll open up a new OTN discussion forum specifically for Oracle R Enterprise focused technical discussions. Stay tuned.”
I’m looking forward to getting my hands on the new Oracle R Enterprise, in 2012. In particular I’m keen to see what additional functionality will be added to the Oracle Data Mining option in the DB.
So watch out for the rebranding to Oracle Advanced Analytics
Charlie – Any chance of an advanced copy of ORE and related DB bits and bobs.
My UKOUG Presentation on ODM PL/SQL API
On Wednesday 7th Dec I gave my presentation at the UKOUG conference in Birmingham. The main topic of the presentation was on using the Oracle Data Miner PL/SQL API to implement a model in a production environment.
There was a good turn out considering it was the afternoon of the last day of the conference.
I asked the attendees about their experience of using the current and previous versions of the Oracle Data Mining tool. Only one of the attendees had used the pre 11g R2 version of the tool.
From my discussions with the attendees, it looks like they would have preferred an introduction/overview type presentation of the new ODM tool. I had submitted a presentation on this, but sadly it was not accepted. Not enough people had voted for it.
For for next year, I will submit an introduction/overview presentation again, but I need more people to vote for it. So watch out for the vote stage next June and vote of it.
Here are the links to the presentation and the demo scripts (which I didn’t get time to run)
Demo Script 1 – Exploring and Exporting model
Demo Script 2 – Import, Dropping and Renaming the model. Plus Queries that use the model







You must be logged in to post a comment.